AI/MLReinforcement LearningCourse Project⭐ Featured
Preference-Guided Meta-RL
Preference-Guided Meta-RL is a framework for learning policies that maximize user preferences using reinforcement learning.
📍 Challenge
Meta-RL algorithms face a fundamental trade-off between generalization and adaptation efficiency. MAML (Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning) requires extensive environmental sampling during fine-tuning, making adaptation costly. PEARL (Efficient Off-policy Meta-learning via Probabilistic Context Variables) enables zero-shot adaptation but sacrifices generalization performance. Existing approaches struggle to balance quick adaptation with robust performance across diverse tasks, limiting their practical applicability in real-world scenarios requiring minimal data.
💡 Motivation
The research addresses the adaptation-generalization dilemma by introducing external guidance through human preferences expressed in natural language. This approach aims to help agents quickly understand new task characteristics without extensive sampling. By incorporating intuitive, high-level instructions, the framework makes Meta-RL more accessible and practical for real-world applications where tasks are diverse and undefined during training.
🔍 Key Findings
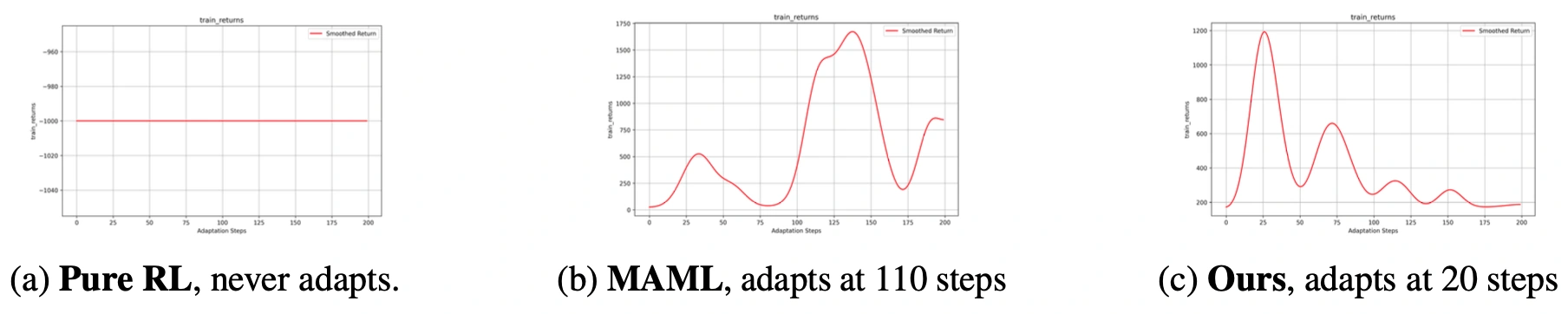
Preference-guided MAML significantly outperforms standard MAML, requiring approximately 50% fewer adaptation steps. The method achieves fastest adaptation (peaks at 20 steps versus MAML's 110 steps). Results demonstrate that incorporating preferences in both training and adaptation stages is superior to using them in only one stage. The approach successfully brings task distributions closer together, reducing adaptation requirements across diverse environments.
🔧 Methods
The framework processes natural language preferences (e.g., "go northeast") through fine-tuned BERT to generate directional preference vectors. These vectors modify the reward function with a cosine similarity term that encourages movement aligned with preferences. A discount factor (αdiscount) gradually reduces directional influence, allowing initial preference-guided exploration followed by independent learning. The approach integrates preferences into both meta-training and adaptation stages of MAML.
📸 Figures
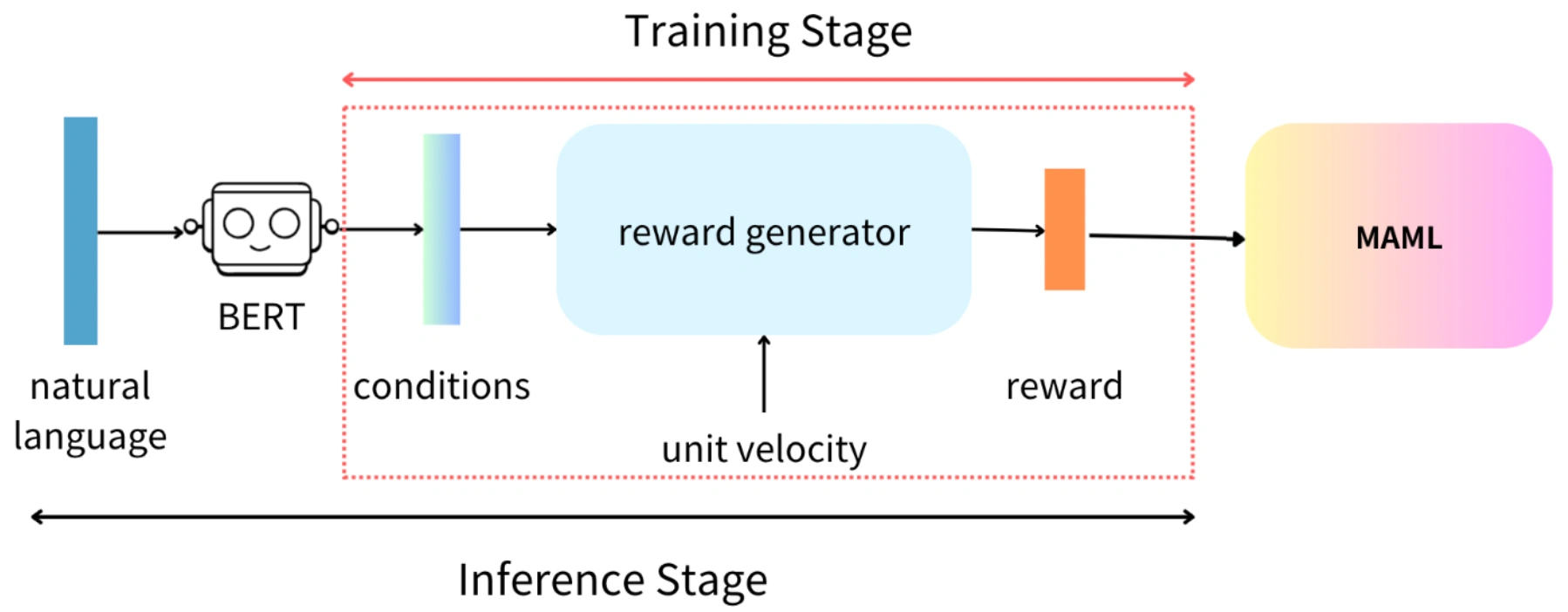
📊 Results

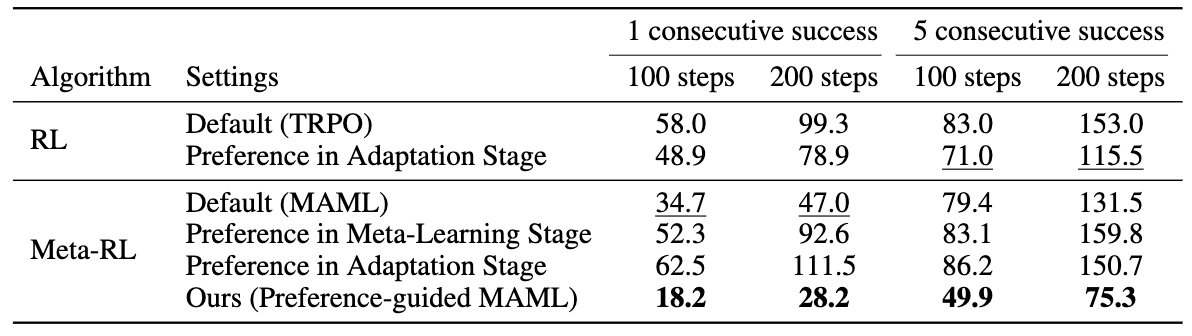
Empty Maze Performance:
- Single success (100 steps): 18.2 steps vs MAML's 34.7 steps (47% reduction)
- Single success (200 steps): 28.2 steps vs MAML's 47.0 steps (40% reduction)
- Five consecutive successes (100 steps): 49.9 steps vs MAML's 79.4 steps (37% reduction)
- Five consecutive successes (200 steps): 75.3 steps vs MAML's 131.5 steps (43% reduction)
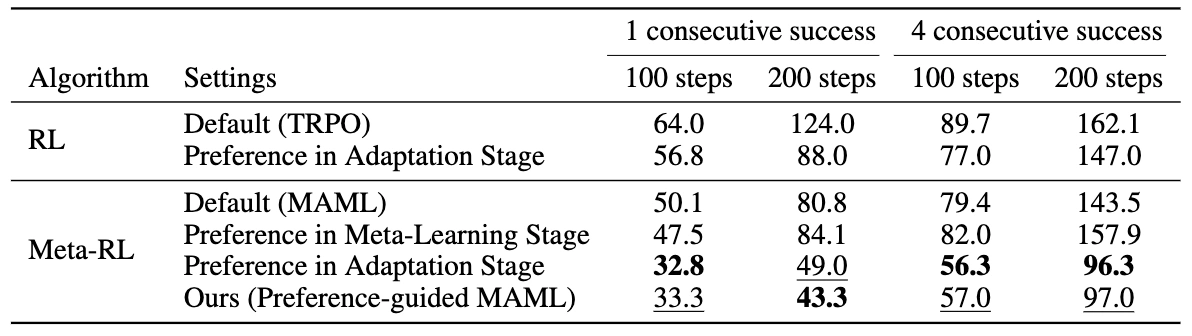
Blocked Maze Performance:
- Single success (100 steps): 33.3 steps vs MAML's 50.1 steps (34% reduction)
- Single success (200 steps): 43.3 steps vs MAML's 80.8 steps (46% reduction)
- Four consecutive successes (100 steps): 57.0 steps vs MAML's 79.4 steps (28% reduction)
- Four consecutive successes (200 steps): 97.0 steps vs MAML's 143.5 steps (32% reduction)
Overall Findings:
- Achieved approximately 50% improvement over pure MAML across environments
- Adaptation peak occurred at 20 steps vs MAML's 110 steps (82% faster)
- Consistently lowest or second-lowest adaptation steps across all configurations
- Meta-RL approaches outperformed pure RL training (TRPO) in all scenarios
- Preference guidance in both stages superior to single-stage implementation
🛠 Tech Stack
PyTorchNumPyGymnasiumBERT
Other Projects
MOSAIC: Exploiting Compositional Blindness in Multimodal Alignment
A novel multimodal jailbreak framework that targets compositional blindness in Vision-Language Models. MOSAIC rewrites harmful requests into Action–Object–State triplets, renders them as stylized visual proxies, and induces state-transition reasoning to bypass safety guardrails. Published at NTU ML 2025 Fall Mini-Conference (Oral).
PEFT-STVG: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Spatio-Temporal Video Grounding
Spatio-Temporal Video Grounding (STVG) localizes objects in video frames that match natural language queries across time. While effective, existing methods require full model fine-tuning, creating significant computational bottlenecks that limit scalability and accessibility.